Structure, Life Cycle, and Economic Importance of Weevil: Comprehensive Guide
Objectives
Weevil/ Beetle
Phylum: Arthropoda
Class: Insecta
Order: Coleoptera
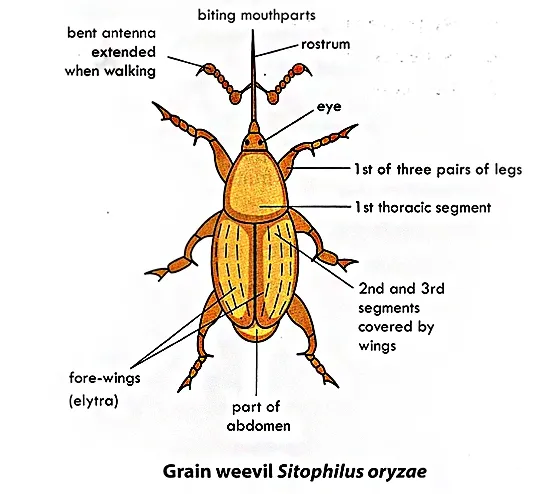
Structure of Weevil
The weevil has a hard exoskeleton which is dark brown in color. It has three body division; the head, thorax and abdomen.
It has chewing mouthparts with well developed mandibles. The mouthparts are elongated and prolonged into a snout called rostrum. The main function of the rostrum is to bore holes in grains, where the female lays their eggs.
It has a pair of jointed bent or elbowed antennae, attached to the mid-length of the rostrum. The antennae end in knob called scape.
The thorax is divided into the prothorax, mesothorax and metathorax. Each segment bears a pair of thick jointed walking legs.
Weevil has two pair of wings. The forewings are hardened and leathery or thickened to form elytra (wing covers). These wings meet in a straight line down the middle of the back. The hind wings are membranous, and are used for flying. When the beetles are not flying, the hind wings are folded under the elytra.
Life Processes of Weevil
Feeding
Weevils are predominantly herbivorous, feeding on a variety of plant materials. Some species are specialized feeders, targeting specific parts of plants like seeds, roots, or stems. The rostrum and mandibles are adapted to their particular diet.
Sensory Perception
Weevils rely on their antennae and compound eyes for navigating their environment, locating food sources, and finding mates. Their sensory organs are highly adapted to their ecological niches.
Life Cycle of Weevil
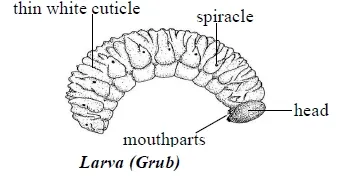
Beetle develops by complete metamorphosis. That is, it has 4 developmental stages: egg, larvae, pupae and adult.
The female uses strong mandibles to chew a hole into a grain after which she deposits a single egg within the hole.
Weevil eggs hatch into soft, pale white or yellow, legless larvae called grubs, which eat the grain material surrounding them.
It pupates within the grain and emerges 2–4 days after hatching. During the pupal stage, it undergoes extreme changes that lead to the development of the adult.
When adult weevils are threatened or disturbed, they pull their legs close to the body and feign death.
Economic Importance of Weevils: Impact and Management
Weevils, belonging to the family Curculionidae, play a significant role in agriculture and the economy. Their impact can be both beneficial and detrimental, depending on the species and their interactions with crops and ecosystems. This guide explores the economic importance of weevils, highlighting their effects on agriculture, forestry, and storage systems, as well as strategies for managing their populations.
1. Agricultural Impact
a. Crop Pests
- Grain Weevils: Species such as the granary weevil (Sitophilus granarius) and the rice weevil (Sitophilus oryzae) are notorious for infesting stored grains. They cause significant losses in cereals like wheat, rice, and corn by boring into kernels and reducing their quality and quantity.
- Boll Weevil: The boll weevil (Anthonomus grandis) is a major pest of cotton crops. It feeds on cotton buds and flowers, leading to reduced yields and substantial economic losses. The boll weevil's impact has historically led to the development of extensive pest control programs.
b. Plant Damage
- Root Weevils: Species such as the black vine weevil (Otiorhynchus sulcatus) and the strawberry root weevil (Otiorhynchus ovatus) damage a variety of crops by feeding on roots. This feeding can lead to plant stunting, reduced yields, and even plant death.
- Fruit Weevils: Some weevils target fruits, causing direct damage and rendering them unmarketable. Examples include the plum curculio (Conotrachelus nenuphar), which affects stone fruits like plums and peaches.
Learn more about agricultural pests and their control on the University of California Agriculture and Natural Resources.
2. Forestry Impact
a. Tree Damage
- Bark and Woodboring Weevils: Species such as the pine weevil (Hylobius abietis) infest forest trees, particularly conifers. They bore into the bark and wood, weakening trees and making them susceptible to diseases and other pests.
- Leaf Weevils: Some weevils feed on tree foliage, causing defoliation and reducing photosynthesis. This can stress trees and reduce their growth and timber quality.
For more information on forestry pests, visit the USDA Forest Service.
3. Stored Product Pests
a. Infestation of Stored Goods
- Granary and Rice Weevils: These weevils are significant pests in storage facilities, where they infest stored grains and cereals. Their presence leads to contamination, reduced quality, and economic losses due to infested products being unsuitable for sale or consumption.
Beneficial Roles
a. Natural Predators
- Weevil Predators: Some weevils are natural predators of other pests. For instance, certain predatory weevils feed on aphids and other soft-bodied insects, providing biological control benefits in agricultural systems.
b. Pollinators
- Pollination: A few weevil species contribute to pollination. For example, the palm weevil (Rhynchophorus ferrugineus) aids in the pollination of certain palm species, playing a role in their reproductive processes.
Learn more about beneficial insects on the Xerces Society for Invertebrate Conservation.
Management Strategies
a. Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
- Biological Control: Utilizing natural predators and parasitoids to control weevil populations. For example, introducing parasitoid wasps can help manage weevil infestations in crops and storage facilities.
- Cultural Control: Implementing crop rotation, sanitation, and resistant crop varieties to reduce weevil impact. Cleaning storage facilities and removing infested materials can also minimize infestations.
b. Chemical Control
- Insecticides: In severe cases, the use of insecticides may be necessary. However, it's important to use them judiciously to minimize environmental impact and prevent resistance development.
- Fumigation: For stored product pests, fumigation can be an effective method to eliminate weevils. This process involves treating infested goods with gaseous pesticides.
Habitat of Weevils: Exploring Their Diverse Environments
Weevils, a large family of beetles known as Curculionidae, are highly adaptable insects that thrive in a wide range of habitats. Their diversity in form and function allows them to exploit various ecological niches, from forests to agricultural fields.
1. Forests
a. Tropical and Temperate Forests
- Leaf Litter and Soil: Many weevils, such as the black vine weevil (Otiorhynchus sulcatus), live in the leaf litter and soil of forests. They feed on roots and decaying plant material, playing a role in nutrient cycling and soil health.
- Tree Bark and Wood: Bark and woodboring weevils, like the pine weevil (Hylobius abietis), inhabit the bark and wood of trees, where they bore into the tree tissues to feed and lay eggs. These weevils can be pests in forestry due to the damage they cause to trees.
For more information on forest habitats and weevils, visit the USDA Forest Service.
2. Agricultural Fields
a. Crops and Vegetation
- Grain Fields: Species such as the granary weevil (Sitophilus granarius) and the rice weevil (Sitophilus oryzae) are found in grain fields. They infest crops like wheat, rice, and corn, feeding on the kernels and causing significant agricultural damage.
- Cotton Fields: The boll weevil (Anthonomus grandis) is a notorious pest in cotton fields. It feeds on cotton buds and flowers, leading to reduced yields and economic losses.
Explore more about agricultural pests and their habitats on the University of California Agriculture and Natural Resources.
3. Gardens and Landscapes
a. Ornamental Plants and Shrubs
- Flower Beds and Shrubberies: Weevils like the strawberry root weevil (Otiorhynchus ovatus) and the black vine weevil are common in gardens, where they feed on the roots and leaves of ornamental plants and shrubs. These weevils can cause significant damage to garden plants, affecting their health and aesthetics.
For tips on managing weevils in gardens, visit the Royal Horticultural Society.
4. Stored Products
a. Storage Facilities
- Granaries and Warehouses: Weevils such as the granary weevil and rice weevil are commonly found in storage facilities, where they infest stored grains and cereals. They can thrive in conditions where grains are stored for long periods, leading to contamination and economic losses.
5. Water Bodies
a. Aquatic Habitats
- Water Weevils: Some weevils, like the rice water weevil (Lissorhoptrus oryzophilus), are adapted to aquatic environments. These weevils live in and around water bodies, such as rice paddies, where they feed on aquatic plants and submerged parts of terrestrial plants.
Adaptations to Different Habitats
a. Morphological Adaptations
- Rostrum: The elongated snout, or rostrum, of weevils is an adaptation that allows them to bore into plant tissues for feeding and egg-laying.
- Legs and Claws: Many weevils have strong legs and claws that help them cling to plants and navigate their environments, whether they are climbing tree bark or burrowing into the soil.
b. Behavioral Adaptations
- Diurnal and Nocturnal Activity: Some weevils are active during the day, while others are nocturnal, helping them avoid predators and optimize their feeding times.
- Camouflage: Many weevils have coloration and patterns that help them blend into their surroundings, providing protection from predators.
Conclusion
The structure of weevils is a marvel of evolutionary adaptation, enabling them to thrive in diverse habitats and fulfill various ecological roles. From their distinctive rostrum to their specialized reproductive systems, each anatomical feature of weevils serves a specific purpose. Understanding these structures and life processes is essential for studying weevil behavior, ecology, and for developing effective pest management strategies.
For further reading on weevil biology and control, visit the USDA's Agricultural Research Service.
By exploring these resources and understanding the intricate anatomy of weevils, we can appreciate their complexity and address the challenges they pose in agriculture and natural ecosystems.
Free Notes on Structure Life Cycle of Weevil
Download Free PDF on: Structure and the Life Processes of Weevil